
Efficient removal of abnormal myelin allows survival of nerve fibers targeted by adaptive immune cells, according to a novel study by scientists of the University Hospital Würzburg.
more
Efficient removal of abnormal myelin allows survival of nerve fibers targeted by adaptive immune cells, according to a novel study by scientists of the University Hospital Würzburg.
more
Setting a new standard in clinical cancer research – that is the goal of Bavarian researchers within the WERA alliance. As of today, the alliance is part of the National Centre for Tumour Diseases (NCT).
more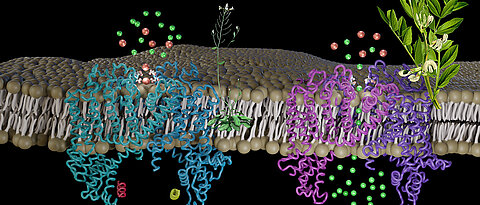
Plants in which an ion channel of the vacuole is hyperactive are extremely stressed and grow poorly. But the broad bean is an exception, as Würzburg researchers have discovered.
more
A new study by Würzburg botanist Kenji Fukushima shows the role of subgenome dominance for plants in the evolutionary development of special traits, such as a carnivorous lifestyle.
more
Physicist Elena Hassinger has been awarded an ERC Consolidator Grant for her research on superconductors. Hassinger is part of the Würzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat.
more
José Pedro Friedmann Angeli has been awarded a European research prize worth two million euros. With his work, the Würzburg professor wants to contribute to innovative therapies against cancer.
more
Junior Professor Anna Lippert from the Institute of Systems Immunology at the University of Würzburg is receiving EUR 10,000 from the Vogel Foundation Dr Eckernkamp to support her research.
more
The Master's degree programmes in management and economics at the University of Würzburg perform very well in the latest Germany-wide ranking by the Centre for Higher Education CHE.
more
Why do students go abroad for a semester or take part in international conferences? A study by the University of Würzburg has investigated this. The results provide recommendations for an internationalisation strategy.
more
Because conventional antibiotics are increasingly failing, researchers at the Helmholtz Institute in Würzburg are looking for new solutions.
more
Where do foreign researchers go when they can freely choose their host university in Germany? This is revealed by the Humboldt Ranking, in which the University of Würzburg is one of the top 20 destinations.
more
Their work is most frequently cited in publications of other scientists. Researchers from the University of Würzburg are therefore included in the Highly Cited Researchers 2023 list.
more
In a new ranking, Computer Science at the University of Würzburg has achieved very good positions in a number of areas. In one discipline, it is even ranked 1st in Germany.
more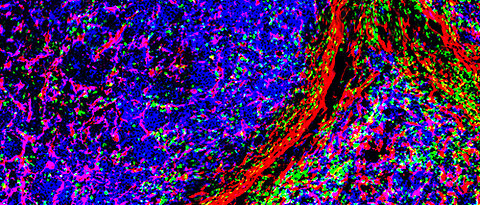
A team of Würzburg cancer researcher Hermann Einsele is part of an international consortium funded by the American Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation with a total of 21 million dollars.
more
Prof Claudia Höbartner from the Institute of Organic Chemistry at the University of Würzburg receives this year's Hansen Family Award for her research on the biomolecular chemistry of functional nucleic acids.
more